What Is AI?
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is an interdisciplinary field combining mathematics, statistics, cognitive science, and computing to solve complex problems using large datasets and high-performance computers.
Within AI, machine learning and deep learning are key subfields. Machine learning involves algorithms that enable systems to learn from data, while deep learning, the most advanced form, closely mimics human intelligence using neural networks.
Examples of AI applications include:
- Self-driving cars
- Speech and facial recognition
- Digital personal assistants
- Chatbots and virtual customer service
- Recommendation engines
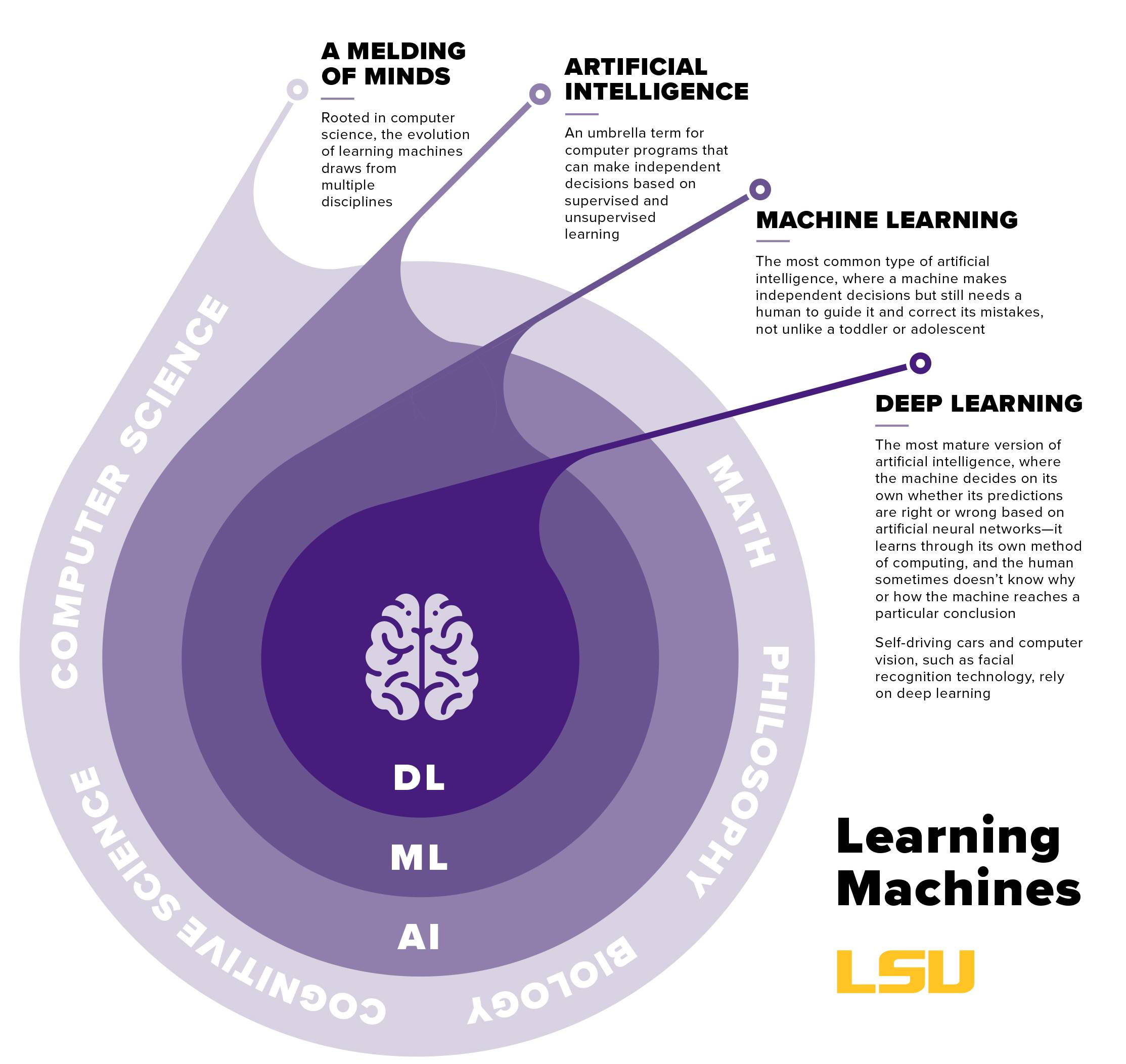
Is it AI or computer science?
Artificial intelligence (AI) incorporates various fields such as computer science, mathematics, philosophy, biology, psychology, and neuroscience. Its applications in research are broad, ranging from infrastructure development and construction to drug discovery, medical diagnosis, and environmental protection. At LSU, researchers across multiple disciplines are leveraging AI to advance their work in diverse fields, applying AI as a powerful tool for problem-solving and innovation.
How does it work?
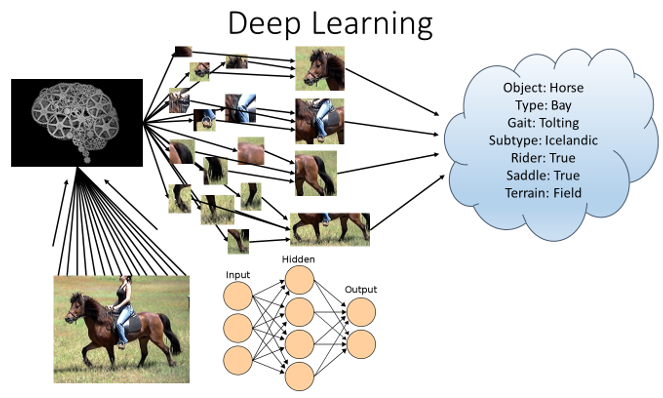
Artificial intelligence (AI) can learn through trial and error, just like humans and animals. When a machine makes a mistake, it learns from it and improves the next time it faces the same problem. AI uses machine learning algorithms to break data into smaller parts to understand new information. There are two types of learning: supervised and unsupervised.
In supervised learning, the AI is given labeled data. For example, if you show it pictures of cats and dogs, at first, it won’t know which is which, so humans help by labeling the images ("this is a cat," "this is a dog"). Over time, the AI learns to recognize the differences on its own, such as cats having whiskers.
Unsupervised learning doesn’t need labeled data, so the machine figures things out on its own, which is becoming more popular since it’s harder to get labeled data.
Deep learning is a type of AI that uses layers of artificial neurons, similar to how the human brain works. Each layer of these networks learns more complex features from the data, like recognizing lines, shapes, and then more detailed things like animals. Deep learning is key in fields like computer vision, which allows AI to "see" the world—important for things like facial recognition and self-driving cars. One big challenge for AI is perception, like recognizing a stop sign that’s partially hidden by shadows, which remains tricky for AI systems to handle correctly.
Is AI safe? (The Terminator question)
Current deep learning systems often don’t clearly explain how they make decisions, which can be a problem when the data they use isn’t accurate. This can happen when the data is noisy or incomplete, and it makes the system’s decisions less reliable. In some cases, attackers might even take advantage of this weakness.
Why AI matters
In simple terms, AI helps us make better decisions by quickly analyzing huge amounts of data, much faster than a human could. It’s really good at recognizing patterns, even ones we might not think to look for.