SAXS / WAXS / GISAXS
Small-Angle X-ray Scattering / Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering / Grazing-Incidence SAXS
What is SAXS?
SAXS is an experimental technique for determining the structure of non-crystalline materials. While X-ray diffraction (XRD) provides information on the atomic scale location of atoms, SAXS provides information on the structure of larger-sacle materials like proteins, micelles, and polymers. SAXS allows one to observe structures such as nanotubes (1D), layered materials (2D), aggregates, and materials like colloids (3D) and can provide information on any order that exists within the structure. When done in grazing incidence, materials like thin-films or the surfaces of cell membranes can be investigated.
Depending on the angles studies, X-ray scattering probes different length scales. WAXS (5-40°) probes structures ~0.1-2 nm, SAXS (0.1-10°) probes 0.5-100 nm while ultra-small SAXS or USAXS (0.01-0.5°) provides information on length scales from 20-1000 nm.
SAXS/WAXS/GISAXS Beamline
|
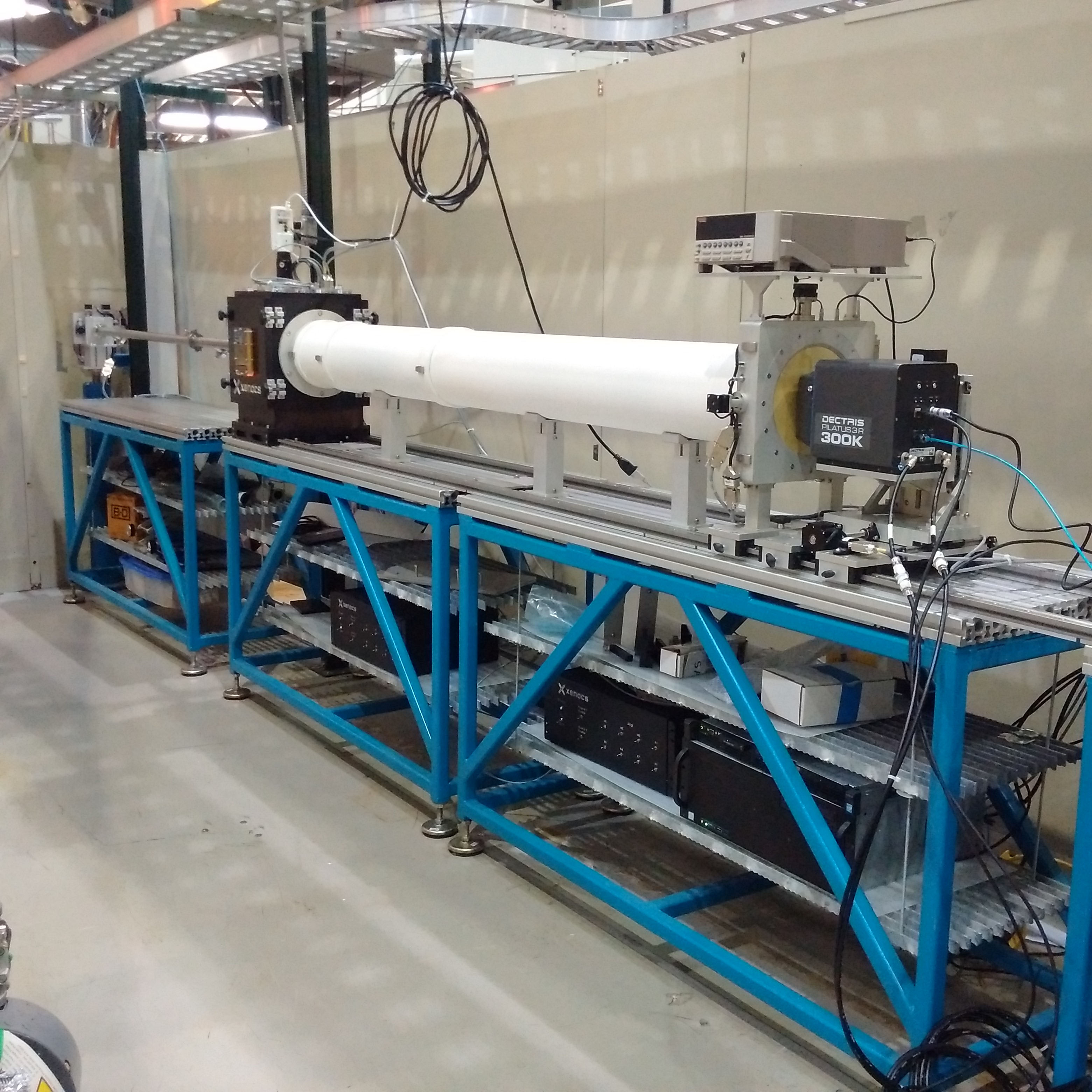
SAXS beamline |
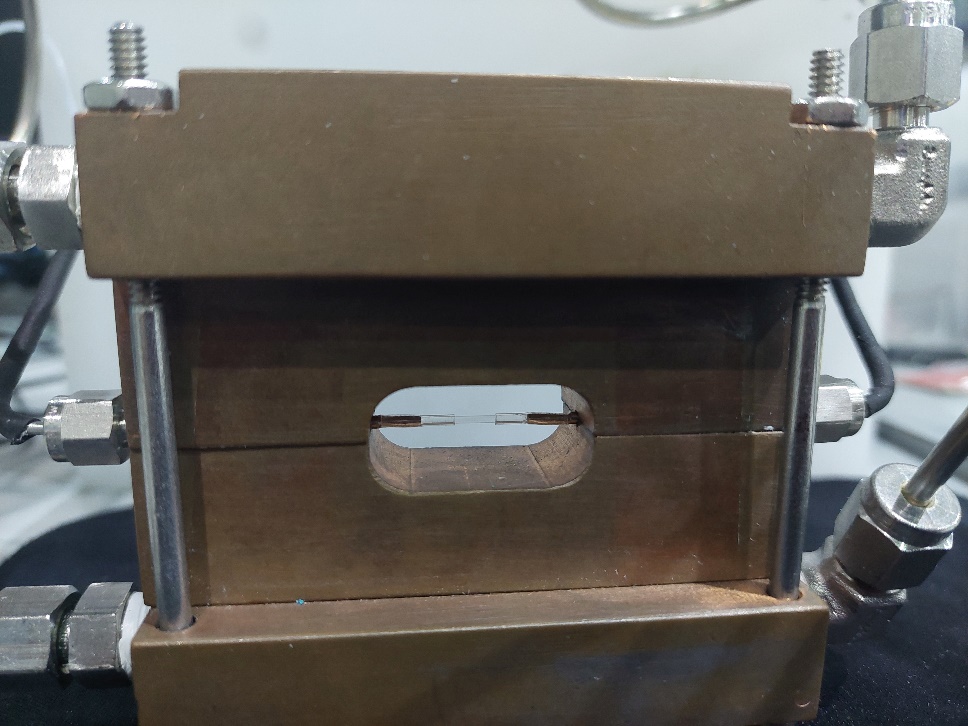
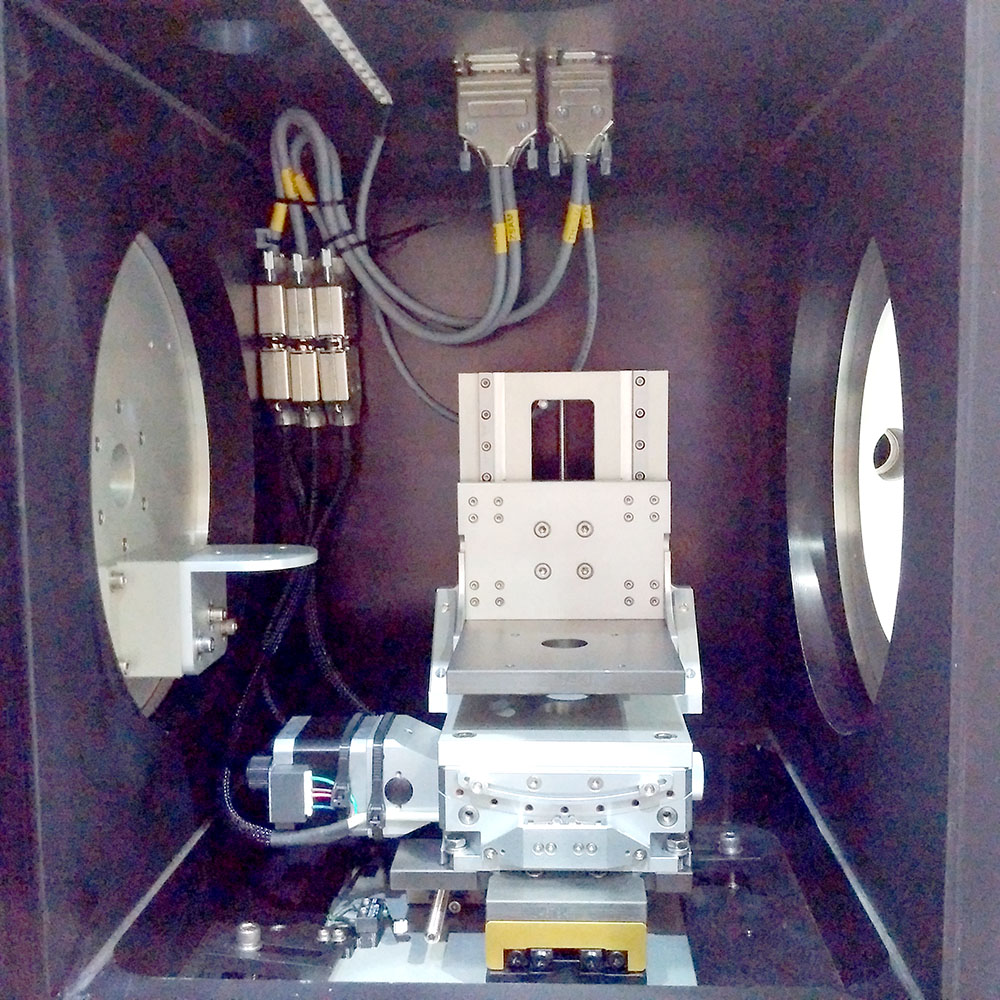
SAXS sample chamber |
At CAMD, the x-ray scattering beamline is located at port 3A-4 which is illuminated by a 7.0T wavelength-shifter insertion device. The monochromator is a double-multilayer equipped with Ru/B4C multilayers (2d = 5 nm) with the photon energy set at 11.7 keV. Higher energies can be used. A set of beryllium lenses located in front of the monochromator partially collimate the beam. Combined with a classical pin hole collimation setup, the percentage of monochromatic and collimated light at the sample position is improved.
The sample chamber with the inner dimensions of 356 mm (H) x 270 mm (W) x 265 mm (D)
can be operated in air, helium and in vacuum. Several feedthroughs allow the installation
of a wide array of sample environments. The sample table allows linear translations
in all dimensions and the tilting required for GISAXS.
The detector in this setup is a Pilatus3 R 300K which has 487 x 619 pixels with a pixel size of 172 x 172 µm2 and an area of 83.8 x 106.5 mm2. The minimal sample-to-detector distance (SDD) is 295 mm with a maximum of 2449 mm, covering the q-range between q = 0.0025 Å-1– q = 0.83 Å-1at 11.7 keV.
Important Q-range settings:
| Flight tube | Sample to detector distance | Q-range |
| none | 263.4. mm | 0.023 - 1.12 A-1 |
| S | 463.4 mm | 0.014 - 0.65 A-1 |
| L | 1563.4 mm | 0.004 - 0.18 A-1 |
| S + M + L | 2417.4 mm | 0.003 - 0.12 A-1 |
|
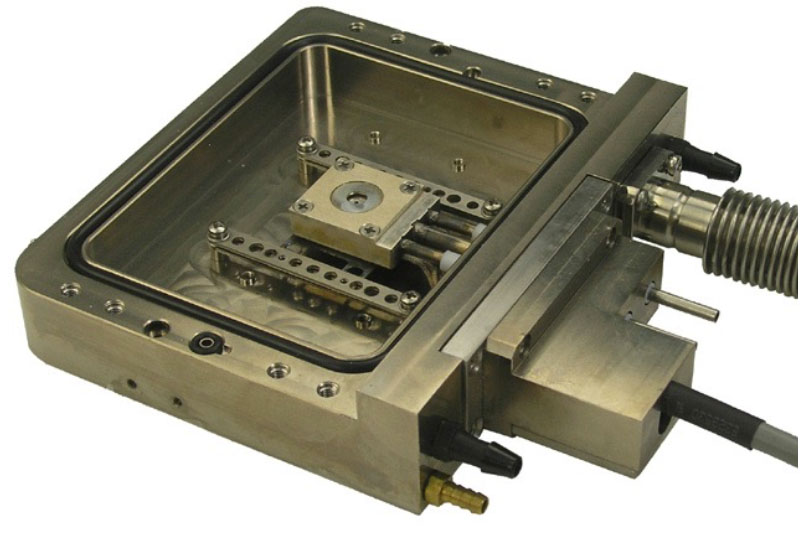
Standard sample plate |
GISAXS sample holder |
Instec temperature cell |
|---|---|---|
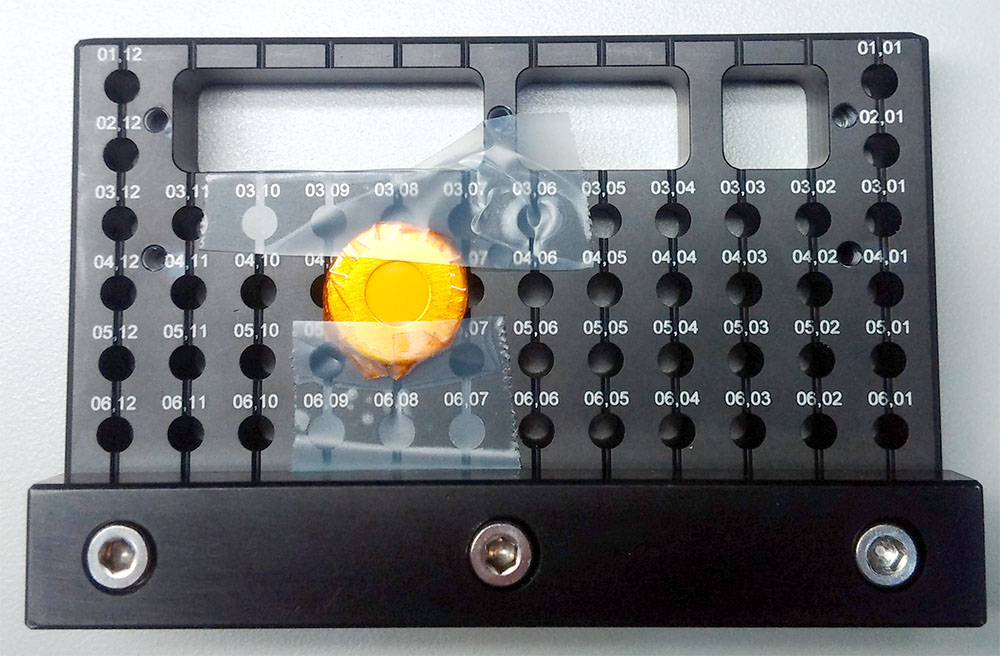

|

|
|
|
Flow through cell: |
Sandwich cell: |
|
|
|
|